Secure Ordering | Free Shipping | 20% Off Retail Prices
Along with providing information on whether exercise recovery supplements might be right for you, this article also links to Fullscript where you can buy supplements for exercise recovery online through the secure healthcare formulary and get free shipping and 20% off the retail price of professional-grade supplements.
Understanding how to optimize post-exercise recovery is crucial for both athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Adding certain nutritional supplements to your routine can help alleviate post-exercise discomfort and enhance recovery. This article explores the scientifically supported benefits of specific supplements aimed at improving recovery, offering valuable insights for enhancing your overall workout regimen.
What Factors Affect Post-Exercise Pain and Recovery?
Post-exercise pain and recovery are influenced by a variety of factors, from your body’s unique physiology to your lifestyle choices. It’s crucial to understand these factors to manage and improve your post-workout recovery effectively. Common signs of post-exercise pain and recovery issues include muscle soreness, stiffness, a reduced range of motion, and unusual fatigue that lasts longer than typical recovery periods. These symptoms often stem from microscopic damage to muscle fibers during intense physical activities, which can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress.
The intensity and duration of your exercise play a major role, with more intense or longer workouts increasing the risk of post-exercise pain. Other important factors that can slow down recovery and enhance discomfort include not getting enough rest, eating poorly, not staying hydrated, skipping proper warm-up or cool-down routines, and pre-existing health conditions. Understanding how these elements interact helps you develop personalized strategies to reduce post-exercise pain and speed up recovery, making your overall fitness journey more effective and enjoyable.
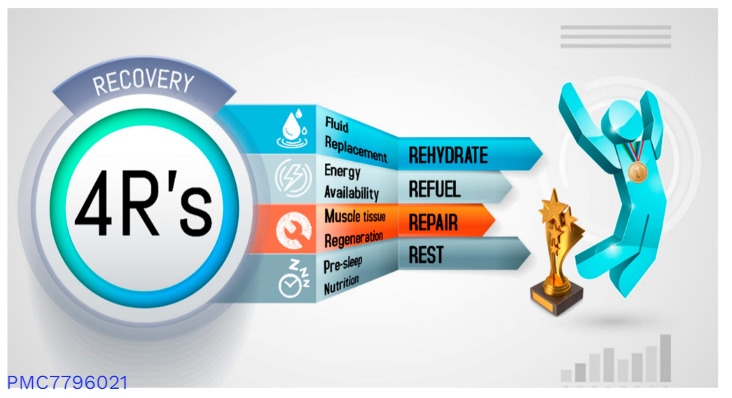
The 4 R’s Of Recovery
Post-exercise recovery aims to restore the body’s ability to perform effectively after physical activity. This involves rehydration, refueling with carbohydrates, repairing muscles with protein and creatine, and ensuring adequate rest, especially with pre-sleep nutrition, to facilitate optimal recovery and performance.
What Food and Lifestyle Factors Are Important For Managing Post-Exercise Pain and Recovery?
- Hydration: Adequate water intake is essential for facilitating the transport of nutrients to muscles and removing waste products, aiding in recovery.
- Balanced Nutrition: Consuming a well-rounded diet rich in lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, healthy fats, and micronutrients supports muscle repair and replenishes energy stores.
- Protein Intake: Protein is crucial for muscle repair and synthesis. Including protein-rich foods such as lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and plant-based sources supports post-exercise recovery.
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Incorporating foods with anti-inflammatory properties, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and omega-3 fatty acids from sources like salmon and flaxseeds, can help reduce inflammation and alleviate post-exercise pain.
- Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is paramount for recovery, as it allows the body to repair and regenerate tissues. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night to optimize recovery.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can impair recovery processes. Engage in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or hobbies to reduce stress levels and promote recovery.
- Active Recovery: Light exercise, stretching, foam rolling, and low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can enhance blood flow, alleviate muscle tension, and expedite recovery without causing further damage.
- Proper Warm-up and Cool-down: Prioritize dynamic stretching and light cardio during warm-up to prepare muscles for exercise and reduce the risk of injury. Cool-down with static stretching to promote flexibility and aid in recovery.
- Consistent Training: Gradually increasing exercise intensity and volume while allowing for adequate rest and recovery between sessions helps prevent overtraining and supports long-term performance gains.
Dietary supplements are not designed to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. This article aims to offer valuable insights into which nutritional supplements have undergone scientific study and shown promise in supporting specific health conditions. We break down the research, so you can work with your medical providers to make informed decisions about adding supplements to your health regimen. For personalized advice tailored to your needs, we recommend consulting with a registered dietitian in addition to your primary care provider.
Check with your physician when adding supplements. While supplements are generally safe for most people, do not add nutritional supplements without your physician’s specific approval if you are pregnant or nursing, are undergoing cancer treatment, have a history of organ transplant, liver or kidney disease, or take medications that interact with supplements.
What Nutritional Supplements Are Recommended For Post-Exercise Pain and Recovery?
- Creatine: Creatine is a naturally occurring compound in muscle cells that helps produce energy during intense exercise. Widely studied and popular among athletes and weightlifters, creatine supplementation enhances short-duration, high-intensity exercise performance, reduces muscle damage, and accelerates post-workout recovery. Overall, it proves effective for enhancing exercise performance and recovery in healthy persons. [PMC8228369]
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil supplements, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation and soreness after intense exercise. They also support overall joint and muscle health. This study investigated the effects of fish oil supplements, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, on muscle recovery after intense exercise and downhill running. Findings revealed that consuming 6 grams of fish oil daily improved jump performance and reduced muscle soreness more effectively than lower doses or a placebo. [PMC7468920] Additionally, omega-3 supplementation reduced muscle soreness 24 hours after exercise but did not influence muscle strength or inflammation markers. [PMC7807509]
- Protein Supplements: Whey protein and plant-based protein supplements are convenient options to ensure adequate protein intake for muscle repair and recovery. Whey protein is often considered the best option for muscle recovery due to its fast absorption and rich content of essential amino acids, which are crucial for stimulating muscle protein synthesis post-exercise. Consuming protein shortly after exercise can enhance muscle protein synthesis and recovery. A study investigated the effects of consuming protein, around the time of exercise on muscle damage from resistance training. Results suggest that protein supplements may help maintain muscle strength and reduce markers of muscle damage after exercise. [PMC10393778]
- Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): BCAAs, including leucine, isoleucine, and valine, are essential for muscle protein synthesis. Taking BCAA supplements before or after exercise can help reduce muscle soreness and promote muscle repair and recovery. The review of 11 studies found that BCAA supplements can lower creatine kinase levels and muscle soreness after exercise. Additionally, a separate study summarized evidence suggesting that BCAA supplementation can reduce muscle damage and soreness after weightlifting in trained men, based on nine studies spanning from 2010 to 2020. These findings show benefits for recovery, as BCAA supplementation was shown to lower creatine kinase levels and decrease soreness within the first-day post-exercise. [PMC8230327]
- Electrolytes: Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium are lost through sweat during exercise. Supplementing with electrolytes may help maintain fluid balance, prevent dehydration, and support muscle function and recovery, especially during prolonged or intense exercise sessions. A study examined the effects of different drinks on hydration and cycling performance after exercise. Participants who consumed the high-electrolyte oral rehydration solution retained more fluids and demonstrated better performance in cycling tests compared to those who drank water or a sports drink. [PMC7765193]
- Magnesium: Magnesium plays a crucial role in muscle function and relaxation. Supplementing with magnesium may help alleviate muscle cramps, reduce soreness, and improve sleep quality, supporting overall recovery. [PMC6723322]
- Curcumin (Turmeric): Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Taking curcumin supplements may help reduce inflammation and promote recovery following exercise-induced muscle damage. A study investigated the effects of curcumin supplementation on athletes’ recovery after exercise. Results showed that athletes who took curcumin experienced less muscle fatigue and soreness after 12 weeks of training, along with improvements in body composition and reduced oxidative stress. [PMC9846492]
- Glutamine: Glutamine is an amino acid that plays a role in immune function and muscle repair. Supplementing with glutamine may help reduce muscle soreness and support recovery, especially during periods of intense training or competition. A study examined if L-glutamine supplements could reduce muscle damage in basketball players. Results showed that those taking glutamine had lower markers of muscle damage compared to those taking a placebo, suggesting protection against exercise-induced muscle damage. [PMC8234492] Intense exercise raises cortisol and leads to leaky gut, whereas glutamine has been found to support gut barrier function potentially leading to better performance. [PMC7982409]
- Beta-Alanine: Beta-alanine is an amino acid that can increase muscle carnosine levels, which may help buffer lactic acid build-up during exercise and reduce fatigue. It is sometimes used to enhance endurance and improve recovery. The International Society of Sports Nutrition reviewed beta-alanine supplements and found they increase muscle carnosine levels, improving exercise performance and reducing fatigue. Although generally safe, tingling is a common side effect, but it can be minimized with lower doses or sustained-release formulas. [PMC4501114]
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D plays a role in muscle function and immune health. Supplementing with vitamin D may help support overall recovery and reduce the risk of muscle injuries, especially in persons with low levels of vitamin D. A study investigated if vitamin D supplements could aid muscle strength recovery after intense exercise. Results showed that vitamin D supplementation increased blood levels and enhanced muscle strength recovery by approximately 8% after a challenging workout, suggesting it may help muscles recover faster in persons with sufficient vitamin D levels. [PMC4029611]
- B-vitamins: B-vitamins, including B6, B12, and folate, are involved in energy metabolism and muscle repair. Supplementing with B vitamins may help support recovery and reduce fatigue after exercise. A study investigated the impact of a 28-day vitamin B complex supplement on exercise performance and fatigue reduction. Results showed significant improvements in running endurance and decreased levels of fatigue-related substances in the blood, suggesting that the supplement may enhance exercise endurance without adverse effects. [PMC10542023]
- HMB (beta-hydroxy beta-methylbutyrate): HMB is a metabolite of the amino acid leucine and is believed to have anti-catabolic properties, meaning it may help reduce muscle breakdown during intense exercise. It is sometimes used to support muscle recovery and promote muscle growth. HMB supplementation has been found to reduce exercise-induced muscle damage and promote recovery by lowering markers of muscle damage and inflammation. It’s typically taken in a daily dose of 3 grams, either regularly for at least two weeks or just before exercise. [PMC9925108]
- Taurine: Taurine is an amino acid that plays a role in muscle function and may help reduce exercise-induced muscle damage and inflammation. It is sometimes included in pre-workout or recovery supplements. Studies suggest that taurine supplements taken before or after exercise could reduce muscle fatigue and soreness, improving recovery, but further research is needed to confirm the most effective supplementation protocol. [PMC5611412]
- Tart Cherry Juice: Tart cherry juice contains antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that may help reduce muscle soreness and inflammation after strenuous exercise. Drinking tart cherry juice before or after exercise may aid in recovery. Cherry juice is often used by athletes for recovery, with studies suggesting that consuming it several days before exercise can speed up muscle recovery afterward. However, starting cherry juice on the day of or after exercise doesn’t seem to have the same benefits, indicating that it may be more effective as a “precovery” drink when consumed before workouts. PMC9306613
- Caffeine: Caffeine is a stimulant that can enhance exercise performance by increasing alertness, reducing perceived exertion, and improving endurance. It may also help reduce post-exercise muscle soreness when consumed in moderation. A study looked at how caffeine affects muscle soreness and performance after upper-body resistance training. They found that taking caffeine before exercise reduced soreness on days 2 and 3 and improved performance during the workout. This suggests that caffeine could help people recover faster from intense exercise and do more training sessions in a short period. PMID: 24164961

When you purchase linked products presented on this page, Supplement Sciences, LLC receives affiliate fees so that our dietitians can continue to create great content.
Thank you for your support!
Order Supplements For Post-Exercise Pain and Recovery
Why Professionals Choose the Fullscript Formulary
Your health is on the line. Health professionals know that many other online and retail options set a very low bar for quality–sometimes amazingly low. The Fullscript formulary is the most secure online source for the highest quality brands securely sourced to assure freshness and purity. Here’s what makes Fullscript the best:
- Meticulous vetting of brand quality. Health professionals trust Fullscript to continuously monitor the quality of each item on the platform. Other retailers operate with profit as their highest or only motive when choosing brands. Fullscript cares only about quality and reliability. Unlike discount stores, large online marketplaces, and other retailers you won’t find ingredients sourced from China or other questionable locations or companies.
- Always 20% Discount off the manufacturer’s retail price. When you follow any link from Supplement-Sciences.com, you will automatically get 20% off the retail price.
- Free shipping over $50.
- Freshness. Fullscript prioritizes freshness over bulk buying even if it means an increased risk of briefly being out of stock.
- Top quality phone and online support. When you call, knowledgeable humans at Fullscript answer your questions.
- How It Works:
- Easy Sign-up & No Spam Email: Click the “View Product” button below to be taken to Fullscript’s login page where you can quickly create your secure account with just your name, email, and phone number. Then you will be taken directly to the product page.
- Wide variety of supplement options: Once you sign in to your account, you are not limited to the products listed below. You will see similar items listed at the bottom of each product page on Fullscript.
- Search For What You Want: Once inside Fullscript, you can search for the exact brands and products you want from their wide selection of quality brands.
Supplement Safety Information
Nutritional supplements can be a safe and valuable tool for supporting post-exercise pain relief and recovery, with many offering benefits backed by scientific research. Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) aid in muscle repair, while creatine enhances strength and endurance without significant adverse effects. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil supplements provide anti-inflammatory properties, promoting joint and muscle health. Protein supplements, tart cherry juice, magnesium, and curcumin offer natural solutions to alleviate soreness and inflammation. Glutamine aids in immune function and muscle repair, and electrolytes help maintain hydration and muscle function during intense workouts. Furthermore, caffeine, vitamin D, B-vitamins, HMB, taurine, and other supplements can enhance performance and recovery with minimal risks when used responsibly. It’s important to adhere to recommended dosages to ensure suitability, especially for persons with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking medications. With proper usage, nutritional supplements can play a safe and effective role in optimizing post-exercise recovery and overall athletic performance.
Medication Interactions:
- NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs): NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin may interact with omega-3 fatty acids, possibly increasing the risk of bleeding due to their combined antiplatelet effects. It’s advisable to use caution when taking NSAIDs and omega-3 supplements together, especially in persons prone to bleeding disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications.
- Anticoagulant medications (e.g., Warfarin): Omega-3 fatty acids may enhance the effects of anticoagulant medications, leading to an increased risk of bleeding. Close monitoring of blood clotting parameters is recommended when combining omega-3 supplements with anticoagulants to prevent excessive bleeding.
- Diuretics (Water Pills): Creatine supplementation may lead to increased water retention, exacerbating the effects of diuretics and causing electrolyte imbalances. It’s important to monitor electrolyte levels and adjust diuretic dosages accordingly when using creatine supplements to prevent dehydration and electrolyte disturbances.
- Lithium: High doses of omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil supplements may increase lithium levels in the blood, possibly leading to lithium toxicity. Close monitoring of lithium levels and adjustment of dosage may be necessary when combining lithium medications with omega-3 supplements to avoid adverse effects.
- Blood Sugar-Lowering Medications (e.g., Metformin, Insulin): Glutamine supplements may affect blood sugar levels, enhancing the effects of blood sugar-lowering medications. Monitoring of blood glucose levels is advisable when combining glutamine supplements with medications used to manage diabetes to prevent hypoglycemia.
- Antidepressant Medications (e.g., SSRIs, MAOIs): St. John’s Wort, sometimes used for its purported antidepressant effects, may interact with antidepressant medications, leading to an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. Caution is advised when combining St. John’s Wort supplements with antidepressant medications to avoid adverse effects associated with serotonin excess.
Supplement Interactions:
- Creatine: Creatine supplementation may enhance the effects of caffeine, increasing alertness and reducing perceived exertion during exercise. This combination may provide a synergistic effect on exercise performance.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil supplements may complement the anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin (turmeric), enhancing their combined effectiveness in reducing post-exercise inflammation and soreness.
- Glutamine: Glutamine supplements may interact with branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), as both are involved in muscle protein synthesis. Combining glutamine with BCAAs may provide additional support for muscle recovery and repair.
- Tart Cherry Juice: Tart cherry juice contains natural melatonin, which may complement magnesium supplements in promoting relaxation and improving sleep quality post-exercise. Combining these supplements may enhance recovery and reduce muscle soreness.
- Electrolytes: Electrolyte supplements such as sodium and potassium may interact with protein supplements by enhancing muscle hydration and promoting nutrient absorption. This combination can support muscle recovery and replenish electrolyte levels depleted during exercise.
Food First!
Although this article discusses supplements in detail, don’t forget that we are absolutely committed to the “Food First” approach to nutrition. When it comes to your health, the totality of your eating habits far surpasses the impact of individual nutrients or any single supplement you consume. Even though this article doesn’t delve into the broader picture of your overall diet, it’s crucial to keep this element at the forefront of our minds. Your food needs to provide all the vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytochemicals to nourish your body systems down to the cellular level.
Food choices, rather than supplements, are the most critical factors for a healthy gut microbiome. These trillions of tiny inhabitants in your gut affect your brain waves; they orchestrate your immune system. They possess the power to create molecules that can switch genes on or off and are even capable of synthesizing neurotransmitters. Opting for organic foods and steering clear of plastic packaging (including those labeled BPA-free) is a smart move to limit toxin exposure. The sum of all these parts leads to a powerful conclusion: the ultimate key to your health lies in the quality and balance of the food you consume. Supplements are secondary.
To Sum It Up
Nutritional supplements offer valuable support for post-exercise pain relief and recovery, empowering people to optimize their fitness goals and overall health. From enhancing muscle repair and reducing inflammation to promoting relaxation and replenishing vital nutrients, these supplements play a crucial role in maximizing the benefits of physical activity. However, it’s essential to approach supplementation with knowledge and caution, considering individual needs. By incorporating the right supplements into a well-rounded lifestyle that includes balanced nutrition, hydration, adequate rest, and consistent training, people can enhance their recovery process and unlock their full potential in achieving their fitness aspirations.
This Article is Not a Substitute for Medical Advice
Dietary supplements are not designed to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The Supplement Sciences website seeks to provide comprehensive access to the most relevant supplement information along with convenient online ordering. We do not provide medical advice and cannot guarantee that every product suggested is completely without risk. Since each person is unique in their health history and medication use, it is important to discuss supplements with your personal physician. Specifically, pregnant women and individuals being treated for cancer or liver or kidney problems must consult their physician about every nutritional supplement they plan to take. People taking medications for the treatment of HIV or with a history of organ transplant must not take supplements without consulting with their physician.

 Scan Me!
Scan Me!

