Secure Ordering | Free Shipping | 20% Off Retail Prices
Along with providing information on whether gout supplements might be right for you, this article also links to Fullscript where you can buy supplements for gout online through Fullscript’s secure healthcare formulary and get free shipping and 20% off the retail price of professional-grade supplements.
In the days of Henry the 8th, gout was a disease of the rich. Since then, our understanding of gout has deepened, shedding light on its intricate relationship with diet, lifestyle, and genetic predisposition. While medications play a crucial role in managing this condition, nutritional supplements may offer a supportive strategy for those seeking additional relief and wellness. This article delves into how certain supplements can complement your gout management plan, offering insights from experts and practical tips to enhance your health journey. By understanding the role of these supplements, people with gout can make informed decisions to may ease their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
What Is Gout?
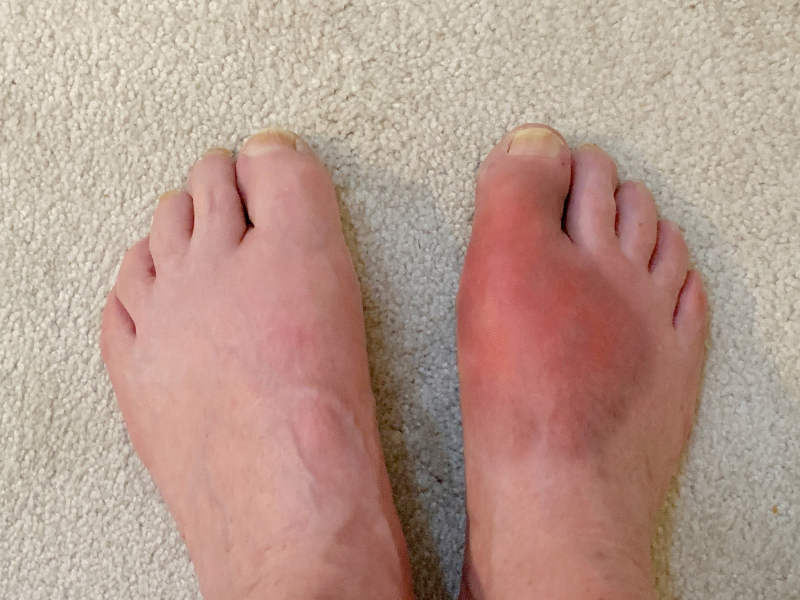
Gout is a type of arthritis that occurs when uric acid, a waste product found naturally in the body, accumulates in the blood and forms crystals in the joints. This condition is characterized by sudden and severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints, often in the big toe. These symptoms typically arise quickly and can be particularly intense during the night. The cause of gout is primarily the buildup of uric acid, which can result from dietary choices (like consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat and seafood), excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, certain medical conditions, and genetic factors. The pain and discomfort of a gout attack are distinctive, and understanding these signs is crucial for individuals to seek appropriate treatment and management strategies.
What Food and Lifestyle Factors Are Important For Managing Gout?
Managing gout involves a combination of dietary adjustments and lifestyle modifications to reduce uric acid levels and prevent flare-ups.
What you eat and drink can play a crucial role in managing gout. Here are the top priorities:
- Avoid Sugary Beverages: Soda sweetened with high fructose corn syrup provides a massive dose of this sugar to the liver. This is linked to increased uric acid levels in the body. Fructose is metabolized in a way that can raise uric acid, potentially triggering gout attacks.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Alcohol consumption, especially beer, has been shown to elevate uric acid levels, contributing to the development and severity of gout attacks. Beer not only contains purines, which are converted into uric acid, but its alcohol content can also slow down the elimination of uric acid from the body.
- Limit High-Purine Foods: Purines are substances found in certain foods that the body breaks down into uric acid. High levels of uric acid can lead to gout. Therefore, reducing the intake of purine-rich foods, including red meats (such as beef and lamb), organ meats (like liver and kidneys), and specific seafood (such as anchovies, sardines, mussels, scallops, trout, and tuna), is advised to help manage uric acid levels.
- Increase Water Intake: Adequate hydration is key in flushing uric acid from the body. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help reduce the concentration of uric acid in the urine and blood, potentially minimizing the risk of gout attacks.
- Cherries: Research suggests that cherries and cherry juice may lower the risk of gout attacks. Cherries contain antioxidants that may help reduce inflammation and uric acid levels, making them a beneficial addition to the diet for individuals with gout.
Lifestyle changes also play a vital role in managing gout, alongside dietary changes:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can increase the body’s production of uric acid and decrease its removal. Weight loss, achieved through a balanced diet and regular exercise, can reduce uric acid levels and lessen the frequency of gout attacks.
- Reduces Uric Acid Production: Excess body fat, especially visceral fat around the abdomen, can lead to increased production of uric acid. Weight loss helps normalize the metabolic processes in the liver, reducing the amount of uric acid produced.
- Improves Liver Function: The liver plays a key role in purine metabolism, converting them into uric acid. Improved liver function, as a result of weight loss, can lead to more efficient uric acid processing and reduced levels in the blood.
- Decreases Inflammatory Response: Excess weight can contribute to a systemic inflammatory state in the body, exacerbating the inflammation caused by uric acid crystals in the joints. Weight loss can reduce inflammation, which in turn can lower uric acid levels and the severity of gout attacks.
- Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Overweight and obesity are associated with insulin resistance, which can impair the kidney’s ability to eliminate uric acid. Weight loss enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing the kidneys to more effectively filter and remove uric acid from the bloodstream.
- Improves Kidney Health: Weight loss can reduce the burden on the kidneys, organs crucial for uric acid excretion. Healthier kidneys are more efficient at filtering uric acid from the blood and excreting it in urine, further lowering blood uric acid levels.
- Regular Exercise: Incorporating regular physical activity not only aids in weight loss but can also improve overall body metabolism, including improving liver health. This can contribute to more effective management of uric acid levels.
- Manage Stress: High stress levels can exacerbate gout symptoms. Implementing stress-reduction strategies, such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises, can help mitigate the impact of stress on gout.
For individuals experiencing frequent or severe gout attacks, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial. Medications may be prescribed to lower uric acid levels or address acute attacks, providing necessary relief and preventing future episodes. Incorporating these dietary and lifestyle changes, along with appropriate medical treatment, can greatly improve the management of gout and enhance quality of life.
What Nutritional Supplements Are Recommended For Gout?
- Quercetin: 500 mg/day. This flavonoid has been studied for its ability to reduce uric acid levels by inhibiting its production and release in the body. Including quercetin-rich foods or supplements may support gout management. [PMC9315272]
- Vitamin C: 500 mg/day. Some studies suggest that vitamin C can contribute to lowering uric acid levels. [PMC9959749]
- Magnesium: Magnesium plays a role in improving kidney function, which is essential for the body’s ability to excrete uric acid efficiently. Adequate magnesium intake may help reduce the risk of gout. [PMID: 32213225]
- Cherry Extract: There is a correlation between cherry intake and reduced gout attacks. [PMC6914931] Cherries and cherry extract had been thought to have the potential to reduce uric acid levels and minimize gout flare-ups. [PMID: 33506357] However, this has not been found consistently and researchers in 2020 found that Tart cherry concentrate (30 ml twice daily for 28 days) had no effect on serum urate or urine urate excretion. They concluded that if there is an effect of cherry concentrate on gout flares, it is not likely to be mediated by a reduction in serum urate. [PMC10687352]
- Green Tea Extract: Rich in antioxidants, green tea extract is believed to possess anti-inflammatory effects. It may play a role in lowering uric acid levels, contributing to gout management. In an animal model, researchers found that EGCG blocked production of free radicals and suppressed gouty inflammation. [PMC6600669]
- Curcumin: Curcumin has potent anti-inflammatory properties. It may help alleviate joint pain and reduce swelling in individuals dealing with gout. [PMID: 37488765]
- More:
- High Dose Omega-3 Fatty Acids: “Dietary n-3 PUFA-rich fish consumption, when adjusted for total purine intake, was associated with lower risk of recurrent gout flares, whereas n-3 PUFA supplementation alone, as taken in a self-directed manner, was not.” [PMC6717014] Omega-3 supplements at a dose of 6.2 grams per day-a very large dose, did reduce gout flares in an open-label trial. [PMC9175343]
- Luteolin: 100 mg/day. Luteolin is a potent flavonoid known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It may help manage gout symptoms by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress associated with high uric acid levels.
Dietary supplements are not designed to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. This article aims to offer valuable insights into which nutritional supplements have undergone scientific study and shown promise in supporting specific health conditions. We break down the research, so you can work with your medical providers to make informed decisions about adding supplements to your health regimen. For personalized advice tailored to your needs, we recommend consulting with a registered dietitian in addition to your primary care provider.
Check with your physician when adding supplements. While supplements are generally safe for most people, do not add nutritional supplements without your physician’s specific approval if you are pregnant or nursing, are undergoing cancer treatment, have a history of organ transplant, liver or kidney disease, or take medications that interact with supplements.
Order Supplements For Managing Gout
Why Professionals Choose the Fullscript Formulary
Your health is on the line. Health professionals know that many other online and retail options set a very low bar for quality–sometimes amazingly low. The Fullscript formulary is the most secure online source for the highest quality brands securely sourced to assure freshness and purity. Here’s what makes Fullscript the best:
- Meticulous vetting of brand quality. Health professionals trust Fullscript to continuously monitor the quality of each item on the platform. Other retailers operate with profit as their highest or only motive when choosing brands. Fullscript cares only about quality and reliability. Unlike discount stores, large online marketplaces, and other retailers you won’t find ingredients sourced from China or other questionable locations or companies.
- Always 20% Discount off the manufacturer’s retail price. When you follow any link from Supplement-Sciences.com, you will automatically get 20% off the retail price.
- Free shipping over $50.
- Freshness. Fullscript prioritizes freshness over bulk buying even if it means an increased risk of briefly being out of stock.
- Top quality phone and online support. When you call, knowledgeable humans at Fullscript answer your questions.
- How It Works:
- Easy Sign-up & No Spam Email: Click the “View Product” button below to be taken to Fullscript’s login page where you can quickly create your secure account with just your name, email, and phone number. Then you will be taken directly to the product page.
- Wide variety of supplement options: Once you sign in to your account, you are not limited to the products listed below. You will see similar items listed at the bottom of each product page on Fullscript.
- Search For What You Want: Once inside Fullscript, you can search for the exact brands and products you want from their wide selection of quality brands.

When you purchase linked products presented on this page, Supplement Sciences, LLC receives affiliate fees so that our dietitians can continue to create great content.
Thank you for your support!
Supplement Safety Information
Cherry extract, vitamin C, omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin, magnesium, quercetin, luteolin and green tea extract are considered safe for people with gout when used appropriately. Cherry extract may help reduce the frequency of gout attacks. Vitamin C supports kidney function, possibly assisting in uric acid excretion. Omega-3 fatty acids can reduce inflammation associated with gout. Curcumin offers anti-inflammatory benefits. Magnesium may improve the body’s handling of uric acid. Quercetin can help lower uric acid levels by improving kidney function. Green tea extract is rich in antioxidants and may support overall health without negatively impacting gout conditions.
Medication Interactions:
- Blood Thinners (e.g., Warfarin, Aspirin)
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: May increase bleeding risk.
- Green Tea Extract: May enhance the effect of blood thinning, increasing bleeding risk.
- Curcumin: Can slow blood clotting, increasing the risk of bruising and bleeding.
- Blood Pressure Medications
- Magnesium: Can have additive effects with medications for high blood pressure, may cause blood pressure to go too low.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: May lower blood pressure, enhancing the effects of these medications.
- Diabetes Medications
- Magnesium: May affect blood sugar levels, requiring adjustments in medication dosages.
- Curcumin: Might lower blood sugar levels in people with diabetes, necessitating medication adjustment.
- Chemotherapy Drugs
- Green Tea Extract: Can may interfere with the mechanism of certain chemotherapy drugs.
- Curcumin: May interfere with the effectiveness of some chemotherapy medications.
- Calcium Channel Blockers
- Magnesium: May have additive effects with these medications, could lead to low blood pressure.
- Liver Metabolized Drugs (CYP450 substrates)
- Quercetin: Can interfere with the metabolism of drugs processed by liver enzymes, affecting drug levels in the blood.
- Green Tea Extract: Contains compounds that can alter the metabolism of drugs processed by the liver.
Supplement Interactions:
- Cherry Extract: No widely reported direct interactions with the other listed supplements, but caution is advised when combining with anti-inflammatory supplements due to additive effects.
- Vitamin C: May enhance iron absorption when taken with supplements containing iron.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Can have additive blood-thinning effects when taken with other supplements known to slow blood clotting, such as green tea extract and curcumin.
- Curcumin: Has additive effects with other anti-inflammatory supplements, possibly increasing the risk of gastrointestinal discomfort or bleeding.
- Magnesium: High doses of magnesium can interact with calcium supplements, may affect the absorption and effectiveness of both minerals.
- Quercetin: May interact with supplements that affect blood clotting, like omega-3 fatty acids and green tea extract, enhancing the risk of bleeding.
- Green Tea Extract: Contains caffeine which can increase the stimulant effects of other supplements containing caffeine, leading to nervousness, jitteriness, and possibly heart palpitations. Can have additive effects with other supplements that lower blood pressure, such as omega-3 fatty acids. Can have additive effects with other supplements that slow blood clotting, increasing the risk of bleeding.
Food First!
Although this article discusses supplements in detail, don’t forget that we are absolutely committed to the “Food First” approach to nutrition. When it comes to your health, the totality of your eating habits far surpasses the impact of individual nutrients or any single supplement you consume. Even though this article doesn’t delve into the broader picture of your overall diet, it’s crucial to keep this element at the forefront of our minds. Your food needs to provide all the vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytochemicals to nourish your body systems down to the cellular level.
Food choices, rather than supplements, are the most critical factors for a healthy gut microbiome. These trillions of tiny inhabitants in your gut affect your brain waves; they orchestrate your immune system. They possess the power to create molecules that can switch genes on or off and are even capable of synthesizing neurotransmitters. Opting for organic foods and steering clear of plastic packaging (including those labeled BPA-free) is a smart move to limit toxin exposure. The sum of all these parts leads to a powerful conclusion: the ultimate key to your health lies in the quality and balance of the food you consume. Supplements are secondary.
What Lab Tests Might Be Helpful In Managing Gout?
Lab tests can play a critical role in diagnosing and managing gout effectively. Here are some essential lab tests that might be helpful:
- Serum Uric Acid Test: Measures the amount of uric acid in the blood. High levels can indicate gout or the risk of developing gouty arthritis. A Uric Acid Blood Test (affiliate link) is available through the NutriScape Lab Shop.
- 24-Hour Urinary Uric Acid Test: Assesses how much uric acid is excreted in the urine over 24 hours. This test helps determine if the body is producing too much uric acid or not excreting enough.
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR): These tests measure inflammation in the body and can help assess the intensity of a gout flare-up.
- Kidney Function Tests: Including blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine tests to assess how well the kidneys are working, since kidney function can affect uric acid levels and vice versa.
- Liver Function Tests: To evaluate overall liver health, which can influence uric acid metabolism.
To Sum It Up
Cherry extract, vitamin C, omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin, magnesium, quercetin, luteolin, and green tea extract offer promising health benefits for people managing gout. These supplements may reduce inflammation, lower uric acid levels, and support overall kidney function, possibly easing gout symptoms and frequency of attacks. However, while the benefits of incorporating these supplements into one’s diet are evident, it’s crucial to approach their use with informed caution. Every person’s health situation is unique, and what works for one may not be suitable for another, especially considering the possible interactions with medications and other supplements.
This Article is Not a Substitute for Medical Advice
Dietary supplements are not designed to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The Supplement Sciences website seeks to provide comprehensive access to the most relevant supplement information along with convenient online ordering. We do not provide medical advice and cannot guarantee that every product suggested is completely without risk. Since each person is unique in their health history and medication use, it is important to discuss supplements with your personal physician. Specifically, pregnant women and individuals being treated for cancer or liver or kidney problems must consult their physician about every nutritional supplement they plan to take. People taking medications for the treatment of HIV or with a history of organ transplant must not take supplements without consulting with their physician.

 Scan Me!
Scan Me!